
1 Control of weld gap
In the high frequency welding process, the strip steel is sent to the welded pipe unit, rolled by multiple rollers, and the strip steel is gradually rolled up to form a circular tube blank with an opening gap. and make the ends of the welding joint flush. If the gap is too large, the proximity effect will be reduced, the eddy current heat will be insufficient, and the intergranular bonding of the weld will be poor, resulting in lack of fusion or cracking. If the gap is too small, the proximity effect will increase, the welding heat will be too large, and the welding seam will be burned; or the welding seam will form deep pits after extrusion and rolling, which will affect the surface quality of the welding seam.
2 Welding temperature control
The welding temperature is mainly affected by the high-frequency eddy current thermal power. According to the formula, the high-frequency eddy current thermal power is mainly affected by the current frequency, and the eddy current thermal power is proportional to the square of the current excitation frequency; and the current excitation frequency has stimulated The influence of voltage, current and capacitance, and inductance. The excitation frequency formula is:
f=1/[2π(CL)1/2]...(1)
In the formula: f-excitation frequency (Hz); C-capacitance in the excitation loop (F), capacitance=electricity/voltage; L-inductance in the excitation loop, inductance=magnetic flux/current.
The above formula shows that the excitation frequency is inversely proportional to the square root of the capacitance and inductance in the excitation loop, or proportional to the square root of the voltage and current. As long as the capacitance, inductance or voltage and current in the loop are changed, the excitation frequency can be changed. The purpose of controlling the soldering temperature. For low carbon steel, the welding temperature is controlled at 1250~1460℃, which can meet the penetration requirement of 3~5mm tube wall thickness. In addition, the welding temperature can also be achieved by adjusting the welding speed.
When the input heat is insufficient, the edge of the heated weld cannot reach the welding temperature, and the metal structure remains solid, resulting in incomplete fusion or incomplete penetration; when the input heat is insufficient, the edge of the heated weld exceeds the welding temperature, resulting in overburning or dripping, causing the weld to form a hole in the high frequency welding process.
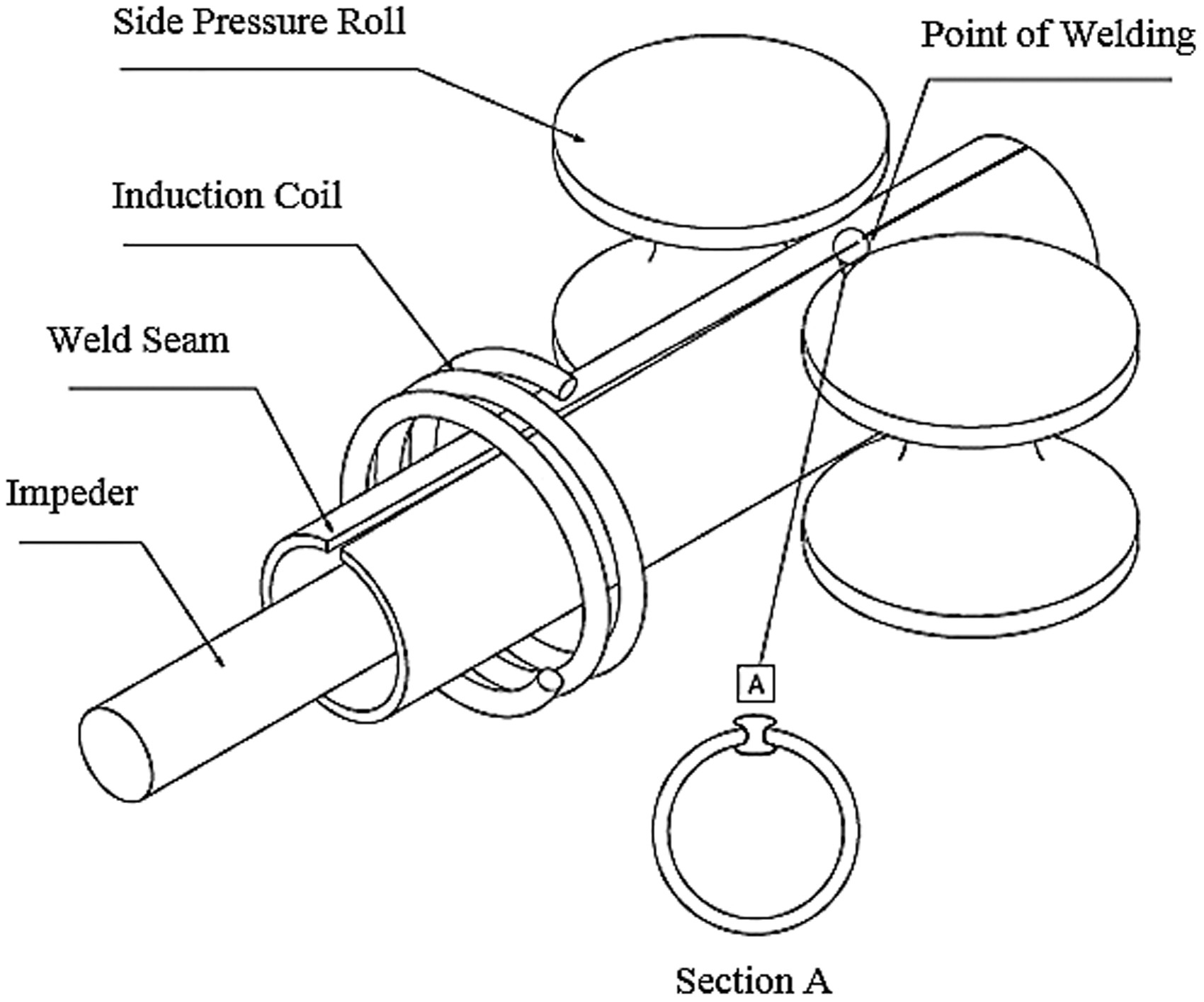
3 Control of extrusion force
After the two edges of the tube blank are heated to the welding temperature, under the extrusion of the extrusion roller, common metal grains are formed to penetrate and crystallize each other, and finally a firm weld is formed. If the extrusion force is too small, the number of common crystals formed will be small, the strength of the weld metal will decrease, and cracking will occur after being stressed; if the extrusion force is too large, the molten metal will be squeezed out of the weld, not only reducing. The strength of the weld is increased, and a large number of internal and external burrs will be generated, and even defects such as welding laps will be caused.
4. Regulation of the position of the high-frequency induction coil
In the high frequency welding process, the high-frequency induction coil should be as close as possible to the position of the squeeze roller. If the induction coil is far from the extrusion roller, the effective heating time will be longer, the heat affected zone will be wider, and the strength of the weld will decrease; on the contrary, the edge of the weld will be insufficiently heated, resulting in poor forming after extrusion.
5 Impedance is one or a group of special magnetic rods for welded pipes. The cross-sectional area of the impedance should usually not be less than 70% of the cross-sectional area of the inner diameter of the seamless square pipe. The electromagnetic induction loop produces a proximity effect, and the eddy current heat is concentrated near the edge of the welded seam of the tube blank, so that the edge of the tube blank is heated to the welding temperature. The resistor is dragged in the tube blank with a steel wire, and its center position should be relatively fixed close to the center position of the extrusion roller. When starting up, due to the rapid movement of the tube blank, the impedance device is greatly lost due to the friction of the inner wall of the tube blank, and needs to be replaced frequently.
6 Weld scars will be produced after welding and extrusion, which need to be removed. The cleaning method is to fix the tool on the frame and scrape the welding scar by the rapid movement of the welded pipe. The burrs inside the welded pipe are generally not removed.